Absolute Risk Reduction Definition. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that women with an average risk of breast cancer BC over 40 get an annual mammogram. Unreported absolute risk reduction measures of 07 and 11 for the PfzierBioNTech and Moderna vaccines respectively are very much lower than the reported relative risk reduction measures. A unique yet easy to use study tool for the USMLE. Absolute Risk Reduction Example.

The absolute risk reductionis the arithmetic difference between the event rates in the two groups. Absolute Risk Reduction ARR Source. In this example the ARR is 8 per cent 20 per cent - 12 per cent 8 per cent. Usually between an exposed and an unexposed group Box 1. Epidemiology A measure of the treatment effect comparing the probabilityor mean of a type of outcome in the control groupwith that of a treatment group. Absolute risk numbers are needed to understand the implications of relative risks and how specific factors or behaviours affect your likelihood of developing a disease or health condition.
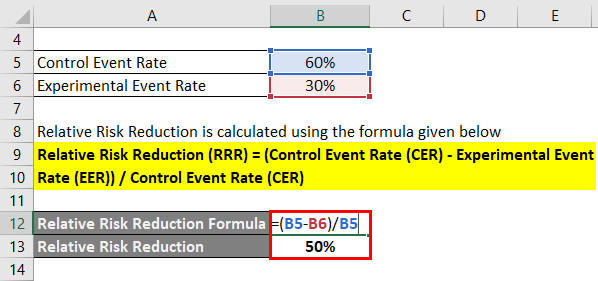
A and 15 die with treatment B the relative risk reduction is 25.
Reporting absolute risk reduction measures is essential to prevent outcome reporting bias in evaluation of COVID-19 vaccine efficacy. The absolute risk reductionis the arithmetic difference between the event rates in the two groups. Absolute risk numbers are needed to understand the implications of relative risks and how specific factors or behaviours affect your likelihood of developing a disease or health condition. In this example the ARR is 8 per cent 20 per cent - 12 per cent 8 per cent. Olly Tree Applications presents USMLE Biostatistics. Usually between an exposed and an unexposed group Box 1.