Define One Tailed Hypothesis. One-tailed hypothesis tests offer the promise of more statistical power compared to an equivalent two-tailed design. Hypothesis tests are used to check a claim about the size of that population proportion. If the sample being tested falls into the one-sided critical area the alternative hypothesis will be accepted instead of the null hypothesis. Statistics - Hypothesis Testing a Proportion Two Tailed Previous Next A population proportion is the share of a population that belongs to a particular category.

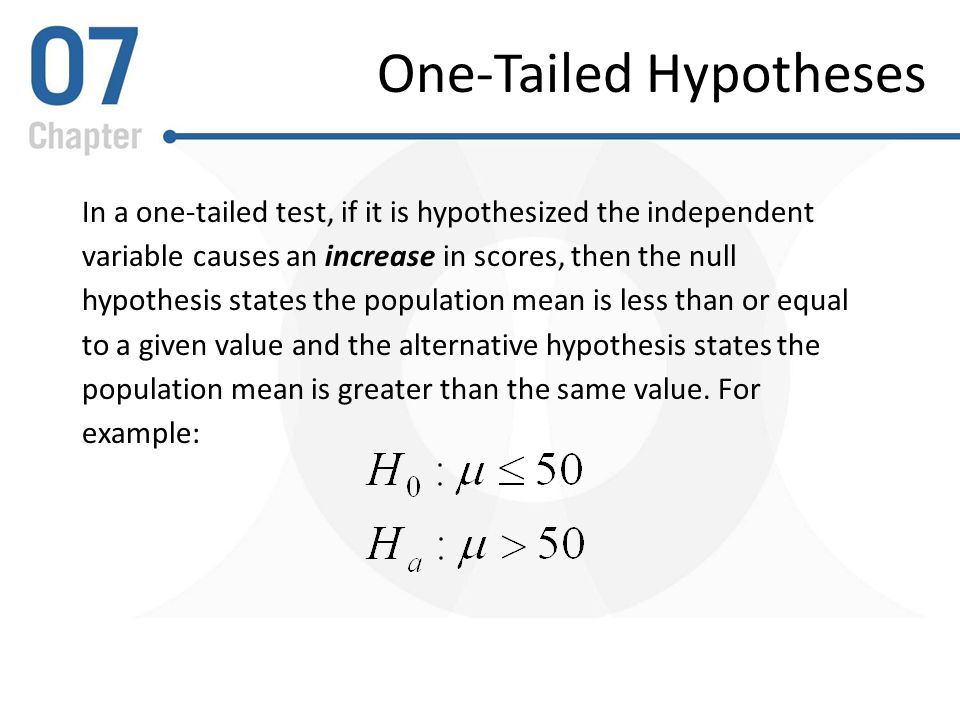
One-tailed hypothesis tests offer the promise of more statistical power compared to an equivalent two-tailed design. In statistics you compare a sample Example. What Is a One-Tailed Test hypothesis. A one-tailed test is a statistical test in which the critical area of a distribution is one-sided so that it is either greater than or less than a certain value but not both. We are not concerned about any upper limit. Hypothesis tests are used to check a claim about the size of that population proportion.
Eg adults will correctly recall more words than children.
A one-tailed test looks for an increase or decrease in the parameter whereas a two-tailed test looks for any change in the parameter which can be any change- increase or decrease. Statistics - Hypothesis Testing a Proportion Two Tailed Previous Next A population proportion is the share of a population that belongs to a particular category. θ0 is a one-sided. One class of high school seniors SAT scores to a larger set of numbers or a distribution the SAT scores for all US high school seniors. A hypothesis test which is designed to identify a difference from a hypothesized value in either direction is called a two-sided test. A one-sided hypothesis is an alternative hypothesis strictly bounded from above or from below as opposed to a two-sided hypothesis which is the union of two one-sided hypotheses and is thus unbounded from both above and below.